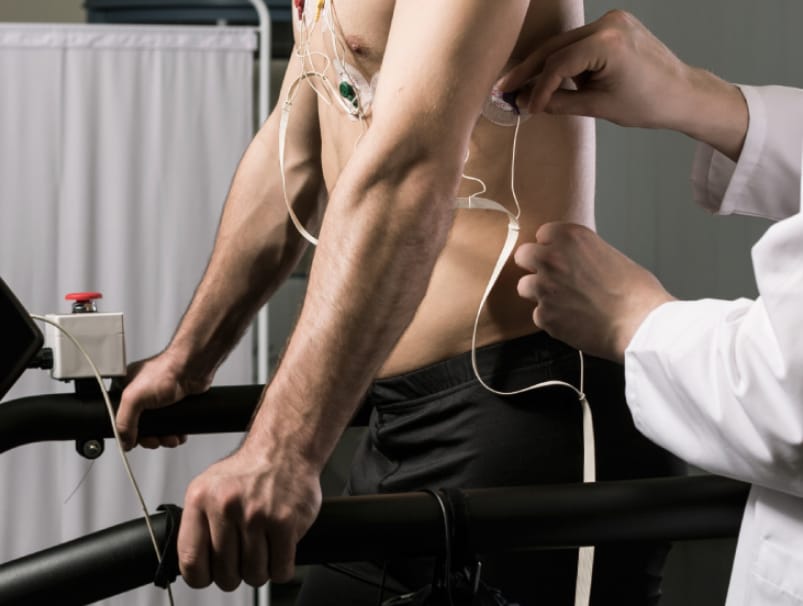
Treadmill stress tests used in conjunction with echocardiography allow for the early detection of significant coronary disease. Areas of the heart which are not receiving adequate blood flow may not contract normally after exercise, and stress echocardiography in conjunction with electrocardiographic changes may be used to detect blockages of the coronary arteries.
Your doctor or Cardiologist may recommend a ‘stress echo’ to:
Investigate the cause of chest pain, shortness of breath, lightheadedness or dizziness.
Investigate for any heart rhythm changes especially during exercise.
Determine your risk of heart disease if you have pre-existing cardiac risk factors like high blood pressure, high cholesterol, family history of heart disease, or diabetes.
Check the effectiveness of coronary artery stents, angioplasty and/or coronary artery bypass surgery.
If you have existing heart disease, an exercise stress echocardiography can assist with planning a safe exercise regime.
Preparation
Fasting is not required but you are advised to have a light meal 2 hours prior to the test.
Wear comfortable walking shoes and clothing such as shorts or active wear.
Procedure
Images of your heart are obtained at rest and immediately after exercising on a treadmill.
The images are then compared side-by-side to detect areas of the heart muscle that are not contracting as vigorously as it should after exercise.
Your blood pressure, heart rate and rhythm are also closely monitored as a response to exercise.
Results
A report will be generated by the Cardiologist, this will then go to your referring doctor usually the same day or overnight if done in the late afternoon. Your Cardiologist will discuss the results with you if you are in consultation and if any follow up is required. You can obtain your results from your referring Doctor or you can request from NSWC reception to send an official copy to you.
Have Questions?
Make an Appointment to get all your cardiology questions answered by our experienced team
Quick and Easy Consultation & Referral Process